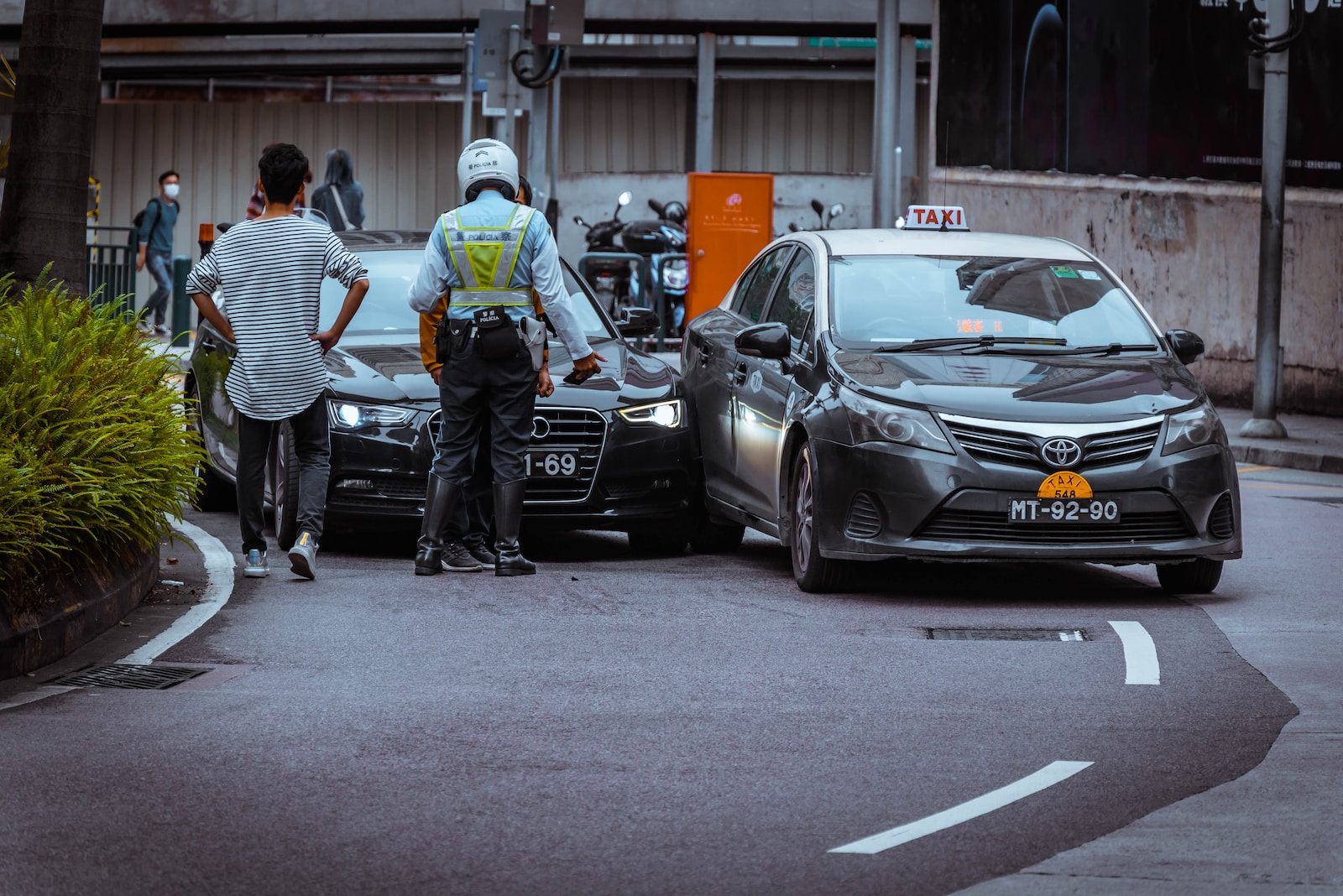
Every day, car accidents occur, leading to physical and emotional pain. The crash can cause immediate harm, but its effects can last a long time. This article looks into “secondary injuries,” which are injuries that happen because of the first trauma experienced in a car accident.
Common Types of Secondary Injuries
Secondary injuries can show up in various ways, affecting different parts of the body and mental well-being. One common type is musculoskeletal injuries, like whiplash, sprains, strains, fractures, and spinal cord injuries. These injuries happen because of the sudden and forceful movements of the body during a crash, causing harm to muscles, ligaments, bones, and joints.
Neurological injuries are another worry after car accidents. Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), ranging from mild concussions to severe brain damage, can occur when the head hits the steering wheel, dashboard, or window. Post-concussion syndrome, which brings headaches, dizziness, and cognitive difficulties, can also happen as a secondary result of TBI. Nerve damage might occur from the compression or stretching of nerves during the accident, causing sensory and motor impairments.
Car accidents can also cause significant psychological trauma beyond physical injuries. The shock and fear during the collision can trigger post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), leading to flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, and depression. Sleep troubles and difficulty concentrating are also common symptoms of psychological trauma after car accidents.
Internal organs are not spared from car accident effects. Lacerations and punctures can happen due to broken glass, sharp metal parts, or the force of the impact itself. Internal bleeding, bruising, and swelling can also occur, potentially leading to life-threatening complications if not dealt with promptly.
The Development of Secondary Injuries
Several factors contribute to the development of secondary injuries after a car accident. The direct impact of the collision can harm organs and tissues, causing immediate injuries like fractures or internal bleeding. Additionally, the indirect impact, such as the body’s rapid and uncontrolled movement during the crash, can result in injuries like whiplash and ligament tears.
Moreover, a chain of effects can lead to further complications. For instance, a broken bone might harm nearby nerves, causing numbness or paralysis. Additionally, delayed complications like blood clots or infections may not show up until days or even weeks after the accident, underscoring the importance of ongoing monitoring and follow-up care.
Factors Influencing the Severity of Secondary Injuries
The seriousness of secondary injuries hinges on several factors, including how severe the initial impact was. According to the Seattle personal injury lawyers from Fang Law Firm, the stronger the collision, the greater the chance of more severe secondary injuries. Additionally, people with pre-existing medical conditions may face a higher risk of complications because of weakened immunity or compromised organ function.
Age is also a factor, as children and older adults are more vulnerable to serious secondary injuries due to their developing or declining physical resilience. Lastly, the timeliness of medical care can have a big impact on the outcome. Early identification and treatment can reduce the severity of secondary injuries and support a quicker recovery.
Strategies for Prevention and Early Detection
Several strategies can help prevent car accidents and reduce the risk of secondary injuries. Wearing seatbelts and having airbags in place can significantly lessen the impact force and lower the potential for injury. Regular car maintenance is important to keep vehicles safe and prevent mechanical issues that could lead to accidents.
It’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly after any car accident, even if there are no apparent injuries. Early medical evaluation can catch and treat potential secondary injuries before they worsen. Individuals should also be aware of signs and symptoms of delayed complications, such as persistent pain, swelling, or changes in mood or behavior, and seek medical attention if they occur.
Car accidents can have far-reaching consequences beyond the immediate collision. Secondary injuries, both physical and psychological, can develop and profoundly affect an individual’s health and well-being. Recognizing the potential for these secondary injuries, understanding how they happen, and taking preventive measures are essential for minimizing their impact and promoting optimal recovery.
By raising awareness and promoting proactive measures, we can strive for a future where the risks associated with car accidents are reduced, and individuals are empowered to recover and thrive after experiencing such trauma.