As technology continues to evolve at record speed, businesses across the United States are upgrading their devices more frequently than ever before. This constant cycle of purchasing and discarding electronics raises an important question: what should companies do with their outdated or broken gear? By choosing to recycle electronics, organizations not only comply with regulatory expectations but also gain financial, environmental, and reputational benefits. Below, we delve into why e-waste recycling is essential for U.S. businesses of all sizes and sectors.
Compliance with Federal and State Regulations
Avoiding Legal and Financial Liabilities
Although there is no single, overarching federal e-waste law, many states have enacted regulations requiring proper disposal of electronic waste. Businesses that fail to comply risk facing fines and other legal liabilities. Additionally, the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) classifies certain electronic components as hazardous waste, requiring safe handling and disposal.
State-Specific E-Waste Laws
Multiple states (including California, New York, Texas, and others) mandate that certain electronics must not be disposed of with regular trash. Instead, they must be directed to approved recyclers or collection sites. By staying informed of state-specific guidelines, companies avoid both legal repercussions and negative publicity.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Secure Disposal of Confidential Information
Outdated electronics—laptops, servers, external hard drives, and smartphones—often contain confidential company data, including customer information, trade secrets, and financial records. Simply tossing or donating these devices without proper data destruction leaves businesses vulnerable to breaches, identity theft, and fraud.
Maintaining Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare or the FTC Disposal Rule for consumer credit information stipulate that organizations must properly dispose of records. Certified electronics recyclers offer services such as data wiping, degaussing, or physical shredding of hard drives, ensuring companies remain compliant with privacy laws and industry standards.
Environmental Stewardship and Corporate Social Responsibility
Mitigating Harmful Toxins
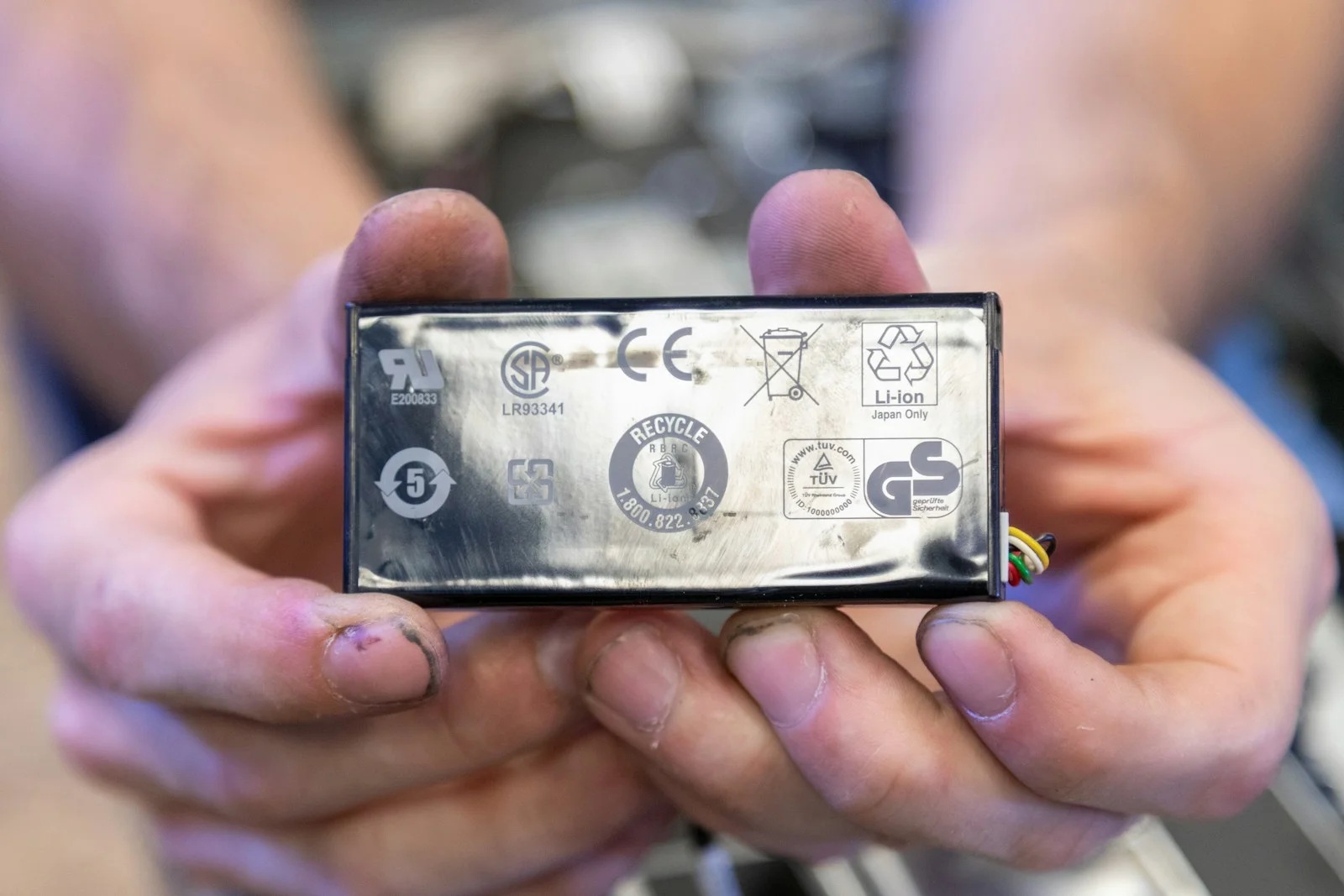
Electronics often contain hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into soil and water if sent to landfills. By partnering with certified recyclers, businesses help prevent these toxins from entering the environment—demonstrating responsible citizenship and a commitment to a healthier planet.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Recycling curtails the need for raw material extraction and heavy manufacturing, both of which require significant energy. By reintroducing valuable metals and plastics into new products, businesses indirectly reduce emissions associated with mining, refining, and production.
Conservation of Valuable Resources
Maximizing Resource Recovery
Electronics contain precious metals such as gold, silver, and copper, as well as rare earth elements. Through recycling, these materials can be reclaimed and used in new devices or other applications, reducing the need for environmentally costly mining efforts.
Supporting a Circular Economy
Modern sustainability practices emphasize transitioning from a “take-make-dispose” model to a more circular approach. By recycling e-waste, businesses contribute to this circular economy, promoting a system that extends product lifespans, saves natural resources, and reduces overall waste.
Enhancing Brand Image and Community Relations
Positive Public Perception
Customers, partners, and investors increasingly expect businesses to act responsibly. Having robust recycling programs—and communicating them effectively—demonstrates that your company prioritizes the environment and ethical practices, strengthening your reputation in the marketplace.
Meeting Stakeholder Expectations
For publicly traded companies, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are gaining prominence. By integrating e-waste recycling into broader sustainability strategies, businesses can meet or exceed stakeholder expectations, ultimately improving investor confidence and community support.
How U.S. Businesses Can Get Started with Electronics Recycling
- Conduct an Inventory Audit
a. Identify all electronic items slated for disposal—computers, monitors, printers, phones, and related accessories. Determine which items have sensitive data that need special handling. - Partner with Certified Recyclers
a. Seek out recyclers certified under strict state licenses. These licenses ensure the recycler adheres to stringent environmental, health, and safety requirements. - Implement Secure Data Destruction
a. Confirm the recycler’s ability to wipe or physically destroy hard drives and other data-storage media. Obtain certificates of data destruction for your records. - Establish an Ongoing Process
a. Develop an in-house policy for e-waste collection, storage, and disposal. Schedule regular pickups or drop-offs with a trusted recycler to avoid equipment piling up over time. - Communicate and Train Employees
a. Educate staff on your organization’s e-waste policy, emphasizing the importance of responsible electronics disposal. Encourage best practices, such as turning in devices for recycling rather than hoarding or throwing them in the trash. - Track and Report
a. Keep records of your recycling totals and data destruction receipts. Sharing these metrics internally (or in public-facing sustainability reports) can boost morale, encourage participation, and strengthen your brand image.
Conclusion
U.S. businesses face a steady stream of electronic upgrades, from essential office computers to advanced data-center equipment. Recycling these devices is no longer a mere option but a strategic move that addresses regulatory obligations, secures sensitive data, protects the environment, and bolsters a company’s public image. By partnering with certified recyclers and integrating e-waste management into broader sustainability efforts, businesses can reap a host of financial, reputational, and operational benefits—while actively contributing to a more sustainable future.