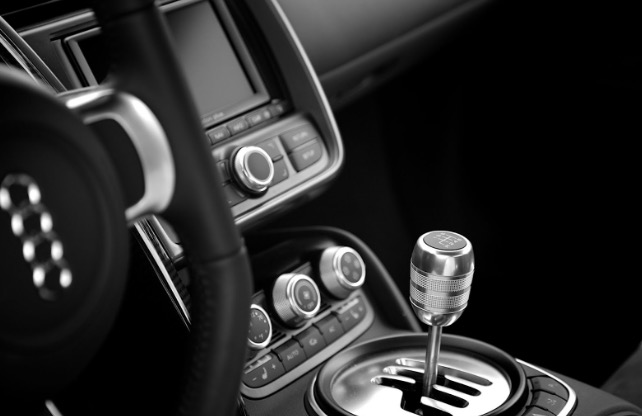
In the realm of automotive engineering, manual transmission cars have long been cherished by enthusiasts for their tactile engagement and precise control. However, beyond the joys of driving stick shift lie intricate mechanisms and potential risks, particularly concerning product liability. Manufacturers of manual transmission vehicles bear significant responsibilities to ensure the safety and reliability of their products.
Legal Framework
Product liability laws govern the responsibilities of manufacturers, distributors, and sellers concerning defective products. In the automotive industry, these laws are crucial for ensuring consumer safety and holding accountable those responsible for any harm caused by their vehicles.
When it comes to manual cars, product liability falls under the broader category of automotive defects. These defects can manifest in various forms, including design defects, manufacturing defects, and marketing defects (failure to warn). Each type of defect carries distinct legal implications.
Design Defects
Design defects occur when a flaw in the vehicle’s design makes it inherently unsafe, even if manufactured precisely according to specifications. In the context of manual cars, design defects may involve issues with the clutch mechanism, gearbox, or pedal assembly. For example, a poorly designed clutch system could lead to premature wear or sudden failure, posing significant safety hazards to drivers and passengers.
Manufacturers have a duty to anticipate potential risks associated with their product designs and take reasonable steps to mitigate them. Failure to do so can result in liability for any injuries or damages resulting from the defect. If you were injured due to the defects of your vehicle, contact a Charleston, West Virginia products liability lawyer to get compensation you deserve.
Manufacturing Defects
Manufacturing defects arise during the production process, leading to individual units being different from the intended design. In manual cars, manufacturing defects may include faulty welds, improperly machined components, or substandard materials. These defects can compromise the vehicle’s structural integrity or mechanical performance, increasing the likelihood of accidents or malfunctions.
From a legal standpoint, manufacturers are strictly liable for any harm caused by manufacturing defects, regardless of whether they were negligent. This principle reflects the idea that manufacturers are in the best position to control the quality of their products and should bear the responsibility for ensuring their safety.
Marketing Defects (Failure to Warn)
Marketing defects occur when manufacturers fail to provide adequate warnings or instructions about the proper use of their products. In the context of manual cars, failure to warn about specific driving techniques or maintenance procedures could result in accidents or injuries. For instance, if a manufacturer neglects to warn drivers about the dangers of “riding the clutch” or improperly shifting gears, they may be held liable for any resulting damages.
Manufacturers have a duty to provide clear and comprehensive instructions for operating their vehicles safely. This includes informing consumers about any risks associated with manual transmission driving and providing guidance on proper maintenance practices to prevent premature wear or component failure.
Manufacturer Responsibilities
Ensuring the safety and reliability of manual cars requires manufacturers to adhere to rigorous quality control standards and proactive risk management strategies. Key responsibilities include:
- Design and Engineering: Manufacturers must conduct thorough testing and analysis during the design phase to identify and address potential safety hazards. This includes simulating various driving conditions and stress testing critical components to assess their durability and performance.
- Quality Assurance: Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures should be implemented to detect and rectify any defects promptly. This involves inspecting raw materials, monitoring production processes, and conducting rigorous testing of finished vehicles to verify their compliance with safety standards.
- Compliance with Regulations: Manufacturers must comply with applicable regulatory requirements governing vehicle safety and performance. This includes adhering to standards set by organizations such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and conducting mandatory safety recalls if defects are discovered post-production.
- Consumer Education: Manufacturers have a responsibility to educate consumers about the proper use and maintenance of manual cars. This includes providing clear instructions in the owner’s manual, offering driver training programs, and disseminating safety advisories as needed to address emerging issues or concerns.
- Prompt Response to Issues: In the event of reported defects or safety concerns, manufacturers should take swift and decisive action to investigate the matter, implement corrective measures, and communicate with affected consumers. This may involve issuing recalls, offering repairs or replacements, or providing compensation for damages incurred.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, manufacturers can uphold their commitment to product safety and mitigate the risk of liability arising from defects in manual cars. Additionally, fostering transparency and accountability within the automotive industry fosters trust and confidence among consumers, ultimately benefiting both manufacturers and consumers alike.
Conclusion
Product liability in manual cars underscores the critical importance of manufacturers’ obligations to ensure the safety and reliability of their products. From design and manufacturing to marketing and consumer education, manufacturers play a central role in safeguarding against defects and minimizing the risk of harm to drivers and passengers. By adhering to stringent quality standards, complying with regulations, and prioritizing consumer safety, manufacturers can uphold their responsibilities and maintain the trust and confidence of consumers in the integrity of manual cars.